Introduction
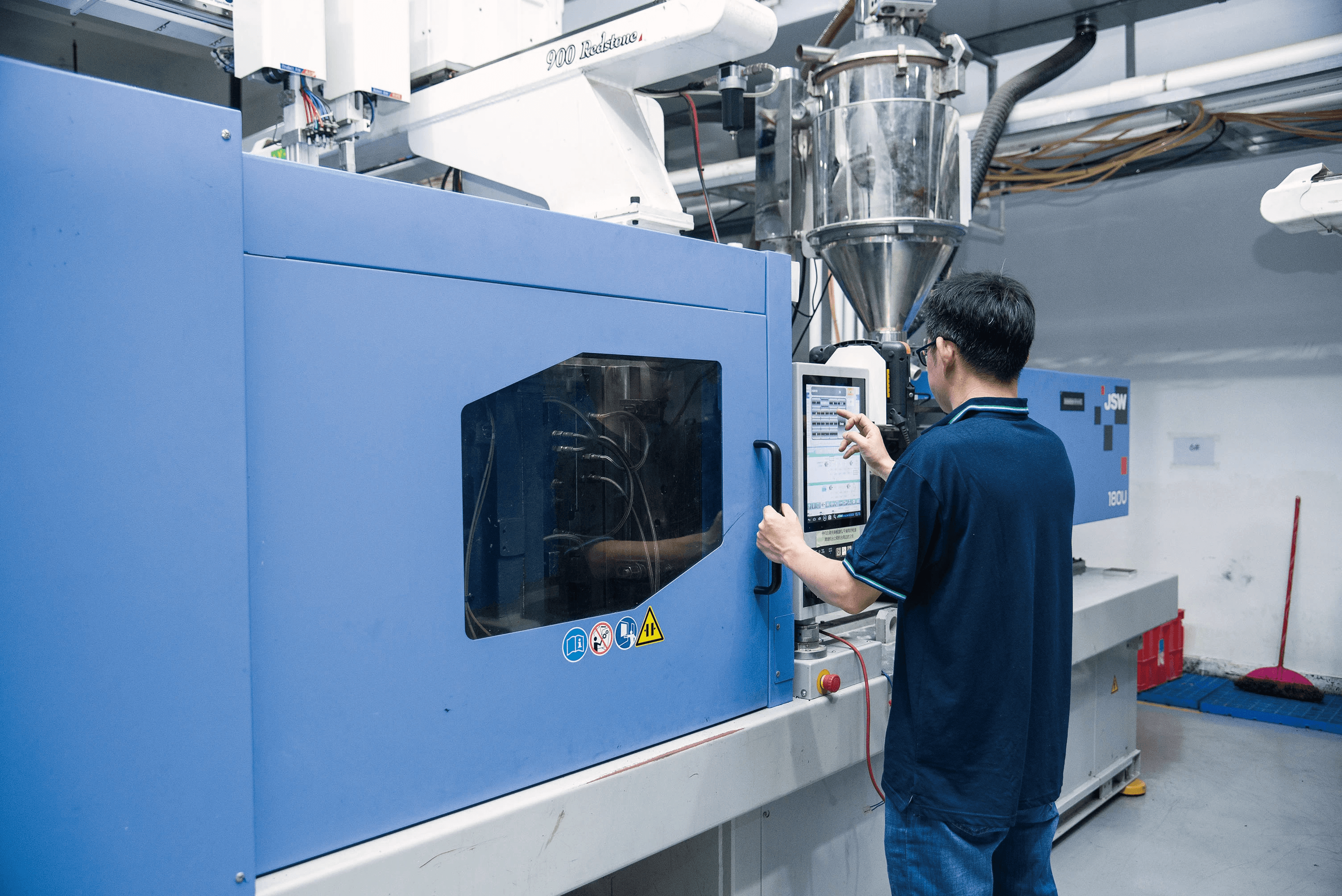
In the world of manufacturing, **PP injection molding** stands out as a versatile and efficient method for creating a wide range of plastic products. Understanding this process is crucial for anyone looking to harness the benefits of Polypropylene (PP) in their projects. From automotive components to consumer goods, PP injection molding offers unique advantages that make it a popular choice among manufacturers.
Understanding the Basics of PP Injection Molding
At its core, **PP injection molding** involves melting Polypropylene pellets and injecting them into a mold to create desired shapes and forms. This process is not just about producing items; it's about precision, efficiency, and scalability. Whether you're asking How to mould PP? or delving into industry applications, grasping the fundamentals will help you appreciate its significance in modern manufacturing.
Key Benefits of Using Polypropylene
Polypropylene boasts several key benefits that make it an attractive option for injection molding. First off, it's lightweight yet strong, which means products can be both durable and easy to handle. Additionally, PP is resistant to chemicals and moisture—two factors that enhance its longevity in various applications—making it a superior choice compared to many other materials.
Overview of the Injection Molding Process
The **injection molding process** begins with heating raw plastic until it reaches a molten state before injecting it into a mold under high pressure. Once cooled, the material solidifies into the final shape—a method that's both efficient and repeatable for high-volume production runs. This technique not only reduces waste but also allows for complex designs that would be challenging with other manufacturing methods.
What is Polypropylene Injection Molding?

Polypropylene injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves the use of polypropylene (PP) as a thermoplastic material to create various shapes and components. This method allows for high precision and efficiency, making it ideal for producing large quantities of parts with consistent quality. With its versatility, PP injection molding has become a go-to solution in many industries.
Definition and Applications of PP
Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its durability and resistance to various chemicals. It can be molded into complex shapes, which makes it suitable for applications ranging from automotive parts to consumer goods. Industries leverage PP's lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness, utilizing it in everything from packaging materials to medical devices.
Advantages of Polypropylene Molding
One of the standout benefits of polypropylene injection molding is its excellent impact resistance, which ensures that products maintain their integrity even under stress. Additionally, PP offers superior chemical resistance compared to many other materials, making it ideal for applications where exposure to harsh substances is common. Furthermore, the recycling potential of polypropylene contributes significantly to sustainability efforts within manufacturing processes.
Common Industries Utilizing PP Injection
Polypropylene injection molding finds application across diverse sectors including automotive, consumer goods, healthcare, and packaging industries. In the automotive realm, it's used for making lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency while maintaining strength. Meanwhile, the consumer goods sector benefits from PP's versatility in creating durable household items such as containers and furniture.
How to Mould PP Effectively

Moulding polypropylene (PP) effectively requires a blend of the right equipment, techniques, and a dash of know-how. Understanding how to mould PP can significantly enhance product quality and production efficiency. This section will guide you through the essential tools, step-by-step processes, and expert tips to achieve optimal results in your pp injection molding endeavors.
Necessary Equipment for PP Molding
To get started with pp injection molding, you'll need a few key pieces of equipment that are essential for successful production. First and foremost is the injection molding machine, specifically designed for thermoplastics like polypropylene (PP). Additionally, you'll require molds tailored to your desired shapes and sizes, temperature control units to maintain ideal conditions, and ancillary equipment such as dryers to prepare your material before processing.
It's also important to have a good cooling system in place since managing heat is crucial during the injection process. The right machinery ensures that you can handle the viscosity of polypropylene effectively while maintaining consistent quality across batches. Lastly, don't forget about safety gear; working with high temperatures and machinery means taking precautions seriously!
Step-by-Step Molding Techniques
Now that you have the necessary equipment lined up, let's dive into step-by-step techniques on how to mould PP effectively using pp injection molding. Start by properly drying your polypropylene pellets if they contain moisture—this is critical since moisture can lead to defects in molded parts. Next, set up your injection molding machine by adjusting parameters such as temperature settings based on what temperature is needed for PP injection molding.
Once everything is prepped and primed, load the dried pellets into the hopper of your machine and initiate the heating process until they reach their melting point. Afterward, inject the molten polymer into your pre-prepared mold under high pressure; this ensures that every nook and cranny gets filled perfectly! Finally, allow sufficient cooling time before ejecting the finished product from the mold—this step cannot be rushed if you want high-quality outputs.
Tips for Optimal Results in PP Injection
Achieving optimal results in pp injection molding doesn’t just come down to following steps; it’s also about fine-tuning various aspects throughout production! One tip is to maintain consistent temperatures throughout both heating and cooling phases—fluctuations can lead to warping or poor surface finish on molded parts. Another important factor is ensuring proper venting in molds; inadequate venting can trap air pockets leading to defects.
Additionally, regularly check material quality before use; any contaminants or inconsistencies could result in subpar products or even machine jams during operation! Lastly, always keep an eye on cycle times—optimizing these can save costs without sacrificing quality over time while also allowing flexibility when comparing materials like PLA vs. PP injection molding when considering project requirements.
Temperature Requirements for PP Injection Molding
Ideal Temperature Settings for PP
The ideal temperature settings for polypropylene injection molding typically range between 180°C and 220°C (356°F to 428°F). These temperatures ensure that the PP material flows smoothly into the mold without compromising its structural integrity. It's important to note that while these are general guidelines, specific applications may require slight adjustments based on factors such as part geometry and wall thickness.
For those wondering how to mould PP effectively, maintaining precise temperatures is key. If temperatures are too low, you risk poor flow properties leading to incomplete filling of molds; too high, and you could degrade the polymer or create surface defects. Therefore, investing in accurate temperature control systems can make all the difference in achieving high-quality results in your pp injection molding projects.
Effects of Temperature on Molding Quality
Temperature plays a vital role in determining the final quality of molded polypropylene products. Too high a processing temperature can lead to issues like burn marks or discoloration, while too low a setting may result in poor surface finish and dimensional inaccuracies. Essentially, finding that sweet spot will enhance both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Moreover, understanding what temperature is needed for PP injection molding can also help avoid common pitfalls such as warping or shrinkage after cooling. The cooling phase must be managed carefully since it directly impacts residual stress within molded parts; improper cooling can lead to deformation over time. Thus, mastering thermal management throughout the entire pp injection molding process is crucial for producing reliable components.
Managing Temperature During the Process
Managing temperature during pp injection molding involves multiple strategies aimed at ensuring uniform heat distribution throughout both material feed zones and molds themselves. One effective approach includes using heated barrels and nozzles—this keeps materials at consistent temperatures before they enter molds. Additionally, employing advanced monitoring systems allows operators to track real-time data on thermal conditions throughout production runs.
Operators should also pay attention to ambient conditions within their facilities; fluctuations in room temperature can affect machine performance and material behavior during processing. Regularly calibrating equipment ensures that your team maintains accuracy when adjusting settings according to specific project needs—after all, precision is paramount! By implementing these best practices for managing temperatures effectively during pp injection molding processes, manufacturers can significantly enhance product quality while minimizing waste.
Comparing PLA and PP Injection Molding
When it comes to injection molding, two materials often come into the spotlight: Polypropylene (PP) and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Understanding the key differences between these two can help manufacturers make informed decisions about which material best suits their needs. In this section, we’ll dive into what sets these polymers apart, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and where each shines in application scenarios.
Key Differences Between PLA and PP
The primary difference between PLA and PP injection molding lies in their composition and properties. PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly choice for many applications. On the other hand, Polypropylene (PP) is a synthetic polymer known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture—qualities that make it ideal for a wide range of industrial uses.
Another significant distinction is temperature resistance; while PP can withstand higher temperatures during processing—typically around 200-230°C—PLA has a lower melting point of approximately 160-180°C. This difference affects how each material behaves during the injection molding process and influences the final product's applications. Ultimately, understanding these key differences can guide manufacturers in choosing the right material based on their specific needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Material
When evaluating pp injection molding versus PLA injection molding, both materials have unique advantages that cater to different market demands. For instance, PP offers superior chemical resistance and can be molded into complex shapes without compromising structural integrity—ideal for automotive parts or containers that require strength under stress. Conversely, PLA’s biodegradability appeals to environmentally conscious consumers looking for sustainable packaging solutions.
However, there are trade-offs to consider as well; while PLA is easier to print with due to its lower melting point, it tends to be less durable than PP when exposed to high temperatures or moisture over time. Additionally, although PP may not decompose as quickly as PLA in natural environments, its recyclability makes it an attractive option for companies aiming for sustainability without sacrificing performance in pp injection molding processes.
Application Scenarios for PLA vs. PP
Understanding application scenarios is crucial when deciding between using polypropylene (PP) or polylactic acid (PLA) in your projects. For example, if you're looking at consumer goods like food packaging or disposable utensils where biodegradability is paramount, then opting for PLA would be wise due to its compostable nature after use. However, if you’re developing robust components such as automotive parts or industrial containers that need durability against harsh conditions—PP would be your go-to material.
Moreover, industries such as healthcare often prefer using pp injection molding with polypropylene due to its sterile properties; this makes it suitable for medical devices that require stringent cleanliness standards. In contrast, creative sectors might lean towards using PLA because of its ease of customization through various colors and textures during the injection process—making products visually appealing while still being eco-friendly.
Exploring Injection Molding Materials

When diving into the world of injection molding, understanding the types of materials available is crucial. Various materials can be employed in injection molding, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Among these, Polypropylene (PP) stands out due to its versatility and favorable properties.
Types of Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding utilizes a range of materials, including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and even metals for specialized applications. Common thermoplastics include ABS, polystyrene, polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP). Each material offers different benefits; for instance, while PE is known for its flexibility and low density, PP injection molding provides superior chemical resistance and durability.
When considering what is the difference between PLA and PP injection molding? It's essential to note that PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable option favored for its eco-friendliness but lacks the strength and heat resistance that PP offers. This distinction makes PP a go-to choice in industries demanding durability without compromising on performance.
Benefits of Using Polypropylene Over Others
Polypropylene boasts several advantages that make it preferable over other materials in many scenarios. Firstly, it has excellent chemical resistance, which ensures longevity in various applications—ideal for automotive parts or packaging solutions where exposure to harsh substances is common. Additionally, PP's lightweight nature combined with high impact strength makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce costs without sacrificing quality.
Moreover, when you ask how to mould PP effectively? The answer lies in understanding its processing requirements—specifically temperature settings—which are critical for achieving optimal results during production. With proper handling techniques and equipment tailored for PP injection molding processes, manufacturers can achieve high-quality outputs consistently.
Case Studies on Material Selection
Examining real-world examples provides insight into how material selection impacts production outcomes. In one case study involving automotive components made from polypropylene (PP) injection molding techniques demonstrated significant improvements in part performance compared to those made from traditional materials like ABS or PE. The decision to use PP resulted not only in enhanced durability but also reduced weight—a key factor in fuel efficiency.
Another example comes from consumer goods manufacturing where companies opted for polypropylene due to its recyclability compared to other plastics like PLA or PE. This choice not only catered to environmental concerns but also appealed to consumers increasingly interested in sustainable products—showing that selecting the right material can align business practices with market trends effectively.
Conclusion
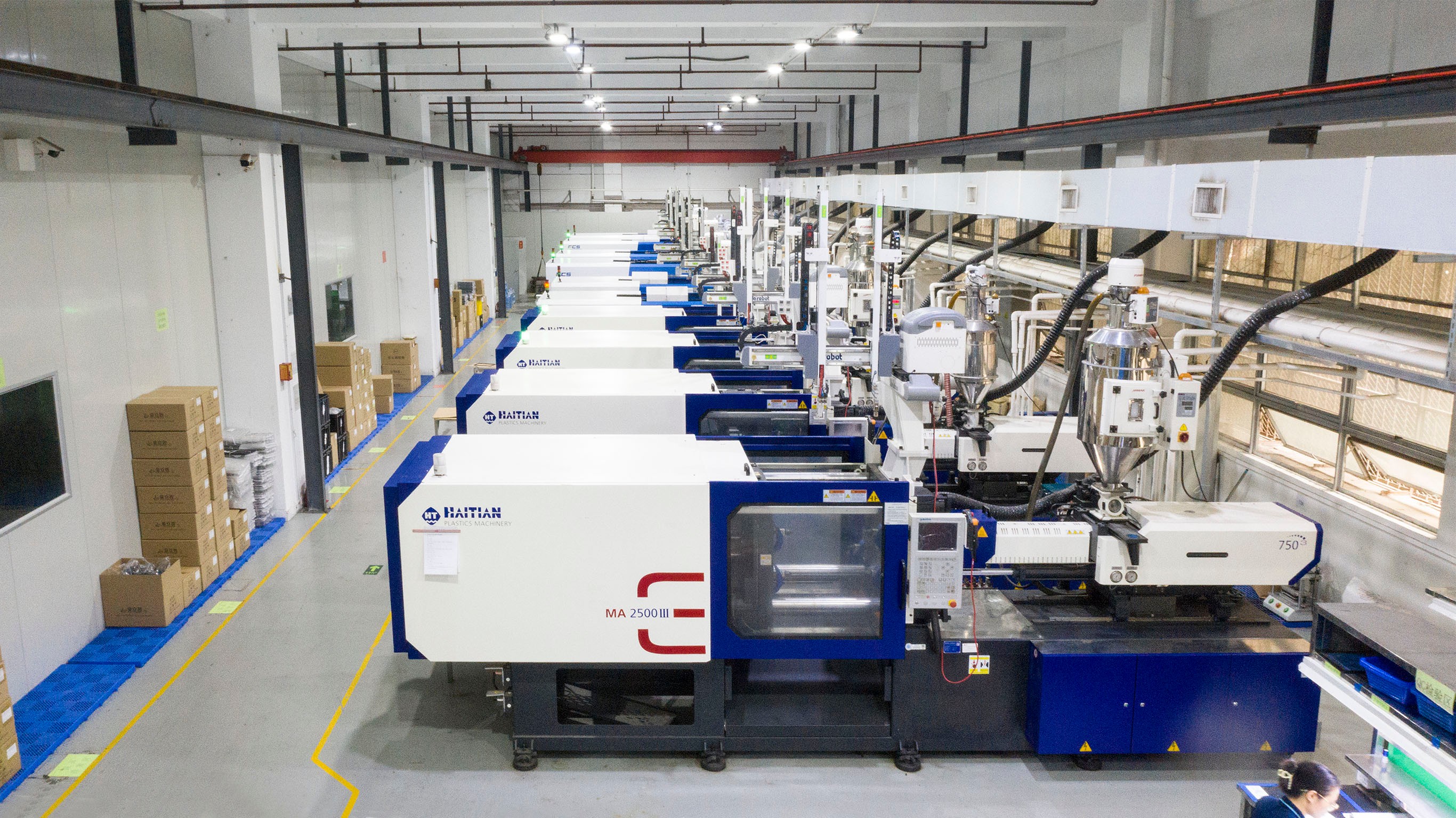

In wrapping up our exploration of polypropylene (PP) injection molding, it's clear that this method is not only versatile but also essential for various industries. As we look to the future, the potential applications and advancements in PP injection molding will continue to grow, driven by innovations in technology and materials science. The emphasis on sustainable practices and efficiency will further enhance the appeal of PP over other materials.
The Future of PP Injection Molding
The future of PP injection molding is bright, with trends leaning towards eco-friendliness and advanced manufacturing techniques. As industries seek more sustainable solutions, polyolefins like polypropylene are gaining traction due to their recyclability and lower environmental impact compared to alternatives like polyethylene or polylactic acid (PLA). Moreover, ongoing research into enhancing the properties of PP means that new applications are on the horizon, making it a material worth watching.
Innovations in Polypropylene Technology
Recent innovations in polypropylene technology have transformed how we approach pp injection molding processes. Enhanced formulations provide improved strength and flexibility while maintaining lightweight characteristics that make PP desirable across various sectors. Additionally, advancements such as bio-based polypropylene are emerging, appealing to environmentally conscious manufacturers looking for alternatives without compromising performance.
Why Choose the Baoyuan Team for Your Needs
When it comes to navigating the complexities of pp injection molding, choosing a reliable partner is crucial—and that's where the Baoyuan team shines! With expertise in both traditional and cutting-edge technologies, they can guide you through every step of how to mould PP effectively while ensuring optimal results with minimal hassle. Their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction makes them an ideal choice for your injection molding materials needs.

